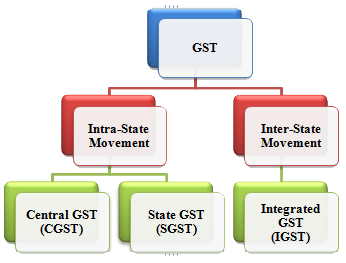
What is GST ?
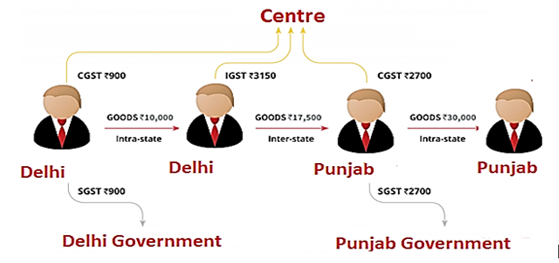
GST is a consumption based tax i.e. the tax should be received by the state in which the goods or services are consumed and not by the state in which such goods are manufactured. IGST will ensure seamless flow of input tax credit between inter-state movements of goods. One state has to deal only with the Center government to settle the tax amounts and not with every other state, thus making the process easier.
For example: A dealer in Punjab sold goods to the consumer in Punjab worth Rs. 10,000. The GST rate is 12% comprising of CGST rate of 6% and SGST rate of 6%, in such case the dealer collects Rs. 1200 and Rs. 600 will go to the central government and Rs. 600 will go to the Punjab government.
Now, if the dealer in Punjab had sold goods to a dealer in Delhi worth Rs. 1, 00,000. The GST rate is 12% comprising of CGST rate of 6% and SGST rate of 6%. In such case the dealer has to charge Rs. 12,000 as IGST. This IGST will go to the Center.
An e-way bill or a consolidated e-way bill generated under this rule shall be valid for the period as mentioned in column (3) of the Table below from the relevant date, for the distance the goods have to be transported, as mentioned in column (2):
| Sr. no. | Distance | Validity period |
| (1) | (2) | (3) |
| 1. | Less than 100 km | One day |
| 2. | 100 km or more but less than 300km | Three days |
| 3. | 300 km or more but less than 500km | Five days |
| 4. | 500 km or more but less than 1000km | Ten days |
| 5. | 1000 km or more | Fifteen days |